Date: 15 Mar 2021

This article provides a brief overview of the main benefits and risks related to home oxygen therapy, covering the most frequently asked questions (FAQ) regarding the use of home oxygen machines regardless of the model. Stay in tune for more on the topic, and do not hesitate to contact our professionals if you've been prescribed oxygen therapy and need to find the most suitable O2 machine for that purpose.
First things first...
What is oxygen therapy and who needs it?
Oxygen is vital for our health. Our cells need oxygen to produce energy. We breath air through our lungs. The oxygen in the air enters our blood and travels to our organs and body tissues.
Oxygen therapy is prescribed for people who can’t get enough oxygen on their own. It is also called supplemental oxygen and it can be used only after a prescription from a health care professional. You can be under oxygen therapy in the hospital or at home. Some people only need it for a short period of time, while others will need it long-term. The need eventually arises due to a given respiratory condition that prevents the lungs from absorbing enough oxygen. These conditions may include the following:
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- pneumonia;
- asthma;
- bronchopulmonary dysplasia, underdeveloped lungs in newborns;
- heart failure;
- cystic fibrosis;
- lung disease;
- trauma to the respiratory system.
 What are the symptoms of low oxygen levels?
What are the symptoms of low oxygen levels?
Doctors measure the oxygen levels in the blood using a pulseoximeter or ABG test. A pulseoximeter is a device that most commonly attaches to the finger and measures the oxygen saturation level in the blood. It also measures the heart rate. The normal levels of saturation are between 94-98%,so any levels below that may be an indication of abnormal lung function. Arterial blood test,remains the most efficient way to monitor the oxygen saturation levels.
When the oxygen levels in your system are low, you’ll experience a variety of symptoms, including:
- rapid breathing;
- shortness of breath;
- fast heart rate;
- coughing or wheezing;
- sweating;
- confusion;
- changes in the color of your skin.
How can I provide oxygen for my needs?
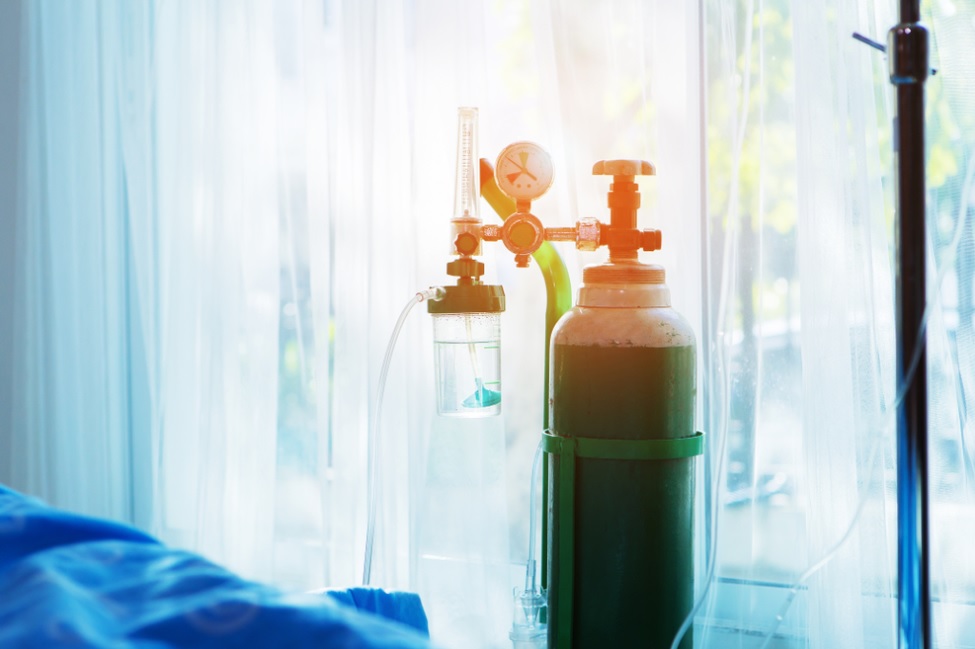
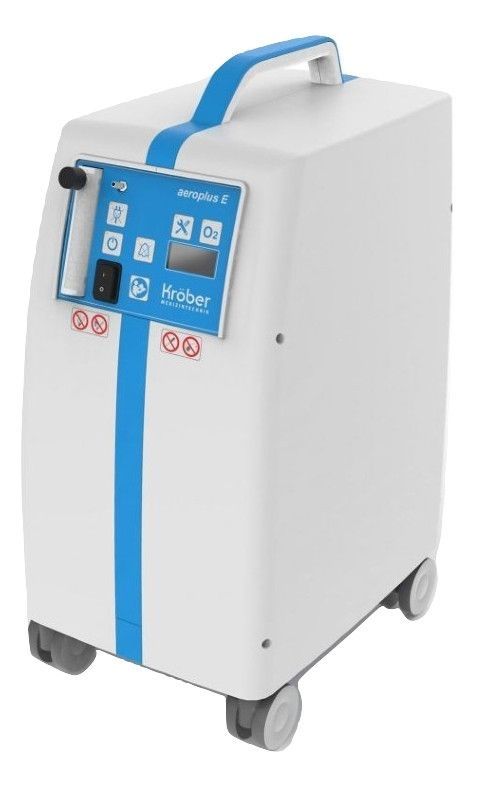
- There are different types of devices for oxygen therapy. Some use tanks of liquid or gas oxygen. Others use an oxygen concentrator, which extracts oxygen from the air in the room. You can get the gas through a nasal cannula or a mask. The extra oxygen is breathed alongside with the air.
- Oxygen concentrators are less portable and heavier than the other options. An oxygen concentrator is a device that extracts oxygen from the room, 'concentrates' it for therapeutic use, and removes other naturally occurring gases.
- The main benefit of home oxygen mahcines is that they virtually don’t require filling likeoxygen tanks do, which saves money and time in the long run. There are also portable models that make traveling while on )2 therapy a breeze.
| Browse Oxygen Concentrators |
What are the risks of using oxygen therapy?
It is very important to consult with your health care provider before using any oxygen device as breathing oxygen for longer periods of time at increased levels can lead to hyperoxia and can cause oxygen toxicity or even oxygen poisoning.
Oxygen toxicity is a condition resulting from the harmful effects of breathing molecular oxygen (O2). There are two types of toxicity:
- Central nervous system toxicity - It's caused by short exposure to high partial pressures of oxygen at greater than atmospheric pressure;
- Pulmonary and ocular toxicity - It results from longer exposure to increased oxygen levels at normal pressure.

Under normal conditions, when oxygen enters the human body, it comes into contact with the hemoglobin in the erythrocytes (Oxyhemoglobin). The hemoglobin carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and organs, and then releases it. But hemoglobin also takes part in carbon monoxide transportation (Carboxyhemoglobin), and when there is a predominant amount of oxygen molecules, the numbers of available hemoglobin are short and the carbon monoxide can't get outside of the human organism.
You should also know that high concentrations of oxygen over a period of time may cause overproduction of free radicals in the lungs.These radicals can severely damage the cell's membrane and destroy lung tissue. If left for a prolonged period of time the patient can suffer permanent lung damage. That's why the patient should be treated with the least amount of oxygen necessary to keep the oxygen levels high enough.
This causes a series of symptoms including:
- anxiety;
- blurred vision;
- dizzines;
- unvoluntery muscle contractions;
- headache;
- nausea.
Summary
Author: Vladimir Atanassov
Editor: Grigor Angelov













Post comment